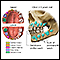
Tooth decay - early childhood
Description
Tooth decay is a serious problem for some children. Decay in the upper and lower front teeth are the most common problems.
Alternative Names
Bottle mouth; Bottle carries; Baby bottle tooth decay; Early childhood caries (ECC); Dental caries; Baby bottle tooth decay; Nursing bottle caries
Keeping Teeth Healthy
Your child needs strong, healthy baby teeth to chew food and to talk. Baby teeth also make space in children's jaws for their adult teeth to grow in straight.
Foods and drinks with sugar that sit in your child's mouth cause tooth decay. Milk, formula, and juice all have sugar in them. A lot of snacks children eat also have sugar in them.
- When children drink or eat sugary things, sugar coats their teeth.
- Sleeping or walking around with a bottle or sippy cup with milk or juice keeps sugar in your child's mouth.
- Sugar feeds the natural forming bacteria in your child's mouth.
- Bacteria produce acid.
- Acid contributes to tooth decay.
Preventing Tooth Decay
To prevent tooth decay, consider breastfeeding your baby. Breast milk by itself is the best food for your baby. It reduces the risk of tooth decay.
If you are bottle-feeding your baby:
- Give babies, ages newborn to 12 months, only formula to drink in bottles.
- Remove the bottle from your child's mouth or hands when your child falls asleep.
- Put your child to bed with a bottle of water only. Do not put your baby to bed with a bottle of juice, milk, or other sweet drinks.
- Teach your baby to drink from a cup at 6 months of age. Stop using a bottle for your babies when they are 12 to 14 months old.
- Do not fill your child's bottle with drinks that are high in sugar, such as punch or soft drinks.
- Do not let your child walk around with a bottle of juice or milk.
- Do not let your baby suck on a pacifier all the time. Do not dip your child's pacifier in honey, sugar, or syrup.
Caring for Your Child's Teeth
Check your child's teeth regularly.
- After each feeding, gently wipe your baby's teeth and gums with a clean washcloth or gauze to remove plaque.
- Begin brushing as soon as your child has teeth.
- Create a routine. For instance, brush your teeth together at bedtime.
If you have infants or toddlers, use a pea-size amount of non-fluoridated toothpaste on a washcloth to gently rub their teeth. When your children become older and can spit out all of the toothpaste after brushing, use a pea-size amount of fluoridated toothpaste on their toothbrushes with soft, nylon bristles to clean their teeth.
Floss your child's teeth when all teeth of your baby come in. This is usually by the time they are 2 ½ years old.
If your baby is 6 months or older, they need fluoride to keep their teeth healthy.
- Use fluoridated water from the tap.
- Give your baby a fluoride supplement if you drink well water or water without fluoride.
- Make sure any bottled water you use has fluoride.
Feed your children foods that contain vitamins and minerals to strengthen their teeth.
Take your children to the dentist when all their baby teeth have come in or at age 2 or 3, whichever comes first.
References
Dhar V. Dental caries. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 338.
Hughes CV, Dean JA. Mechanical and chemotherapeutic home oral hygiene. In: Dean JA, ed. McDonald and Avery's Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA; 2022: chap 8.
Baumhardt H, Chapman B, D'Alesio A, Woods K. Oral disorders. In: Zitelli, BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 21.
Review Date:1/24/2022
Reviewed By:Michael Kapner, DDS, General Dentistry, Norwalk Medical Center, Norwalk CT. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.