Central venous catheters - ports
Definition
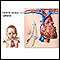
A central venous catheter is a tube that goes into a vein in your arm or chest and ends at the right side of your heart (right atrium).
If the catheter is in your chest, sometimes it is attached to a device called a port that will be under your skin. The port and catheter are put in place in a minor surgery.
The catheter helps carry nutrients and medicine into your body. It can also be used to take blood when you need to have blood tests. Having a port attached to your catheter will cause less wear and tear on your veins than just having the catheter.
Alternative Names
Central venous catheter - subcutaneous; Port-a-Cath; InfusaPort; PasPort; Subclavian port; Medi - port; Central venous line - port
What is the Purpose of a Central Venous Catheter and Port?
Central venous catheters with ports are used when you need treatment over a long period of time. For example, you may need:
- Antibiotics or other medicines for weeks to months
- Extra nutrition because your bowels are not working correctly
Or you may be receiving:
- Kidney dialysis several times a week
- Cancer drugs often
Your health care provider will talk with you about other methods for receiving medicine and fluids into a vein and will help you decide which one is best for you.
Placing the Port
A port is placed under your skin in a minor surgery. Most ports are placed in the chest. But they may also be placed in the arm.
- You may be placed into a deep sleep so you do not feel pain during surgery.
- You may stay awake and receive medicines to help you relax and numb the area so you do not feel pain.
You can go home after your port is placed.
- You will be able to feel and see a quarter-sized bump under your skin where your port is.
- You may be a little sore for a few days after surgery.
- Once you have healed, your port should not hurt.
Taking Care of and Using Your Port
Your port has 3 parts.
- Portal or reservoir. A pouch made of hard metal or plastic.
- Silicone top. Where a needle is inserted into the portal.
- Tube or catheter. Carries medicine or blood from the portal to a large vein and into the heart.
To get medicine or nutrition through your port, a trained provider will stick a special needle through your skin and the silicone top and into the portal. A numbing cream can be used on your skin to decrease the pain of the needle stick.
- Your port may be used in your home, in a clinic, or in the hospital.
- A sterile dressing (bandage) will be placed around your port when it is used to help prevent infection.
When your port is not being used, you can bathe or swim, as long as your doctor says you are ready for activity. Check with your provider if you plan to do any contact sports, such as soccer and football.
Nothing will stick out of your skin when your port is not being used. This decreases your chance of infection in or around your port.
About once a month, you will need to have your port flushed to help prevent clots. To do this, your provider will use a special solution.
Ports can be used for a long time. When you no longer need your port, your provider will remove it.
When to Call the Doctor
Tell your provider right away if you notice any signs of infection, such as:
- Your port seems to have moved.
- Your port site is red, or there are red streaks around the site.
- Your port site is swollen or warm.
- Yellow or green drainage is coming from your port site.
- You have pain or discomfort at the site.
- You have a fever over 100.5°F (38.0°C).
References
Dixon RG. Subcutaneous ports. In: Mauro MA, Murphy KPJ, Thomson KR, Venbrux AC, Morgan RA, eds. Image-Guided Interventions. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 85.
James D. Central venous catheter insertion. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 228.
Witt SH, Carr CM, Krywko DM. Indwelling vascular access devices: emergency access and management. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 24.
Review Date:4/17/2022
Reviewed By:David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.