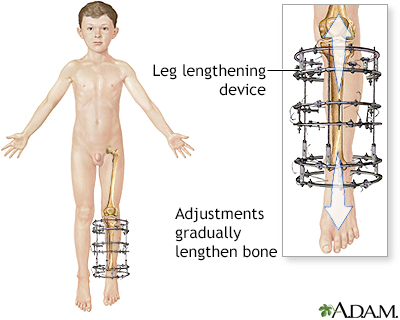
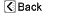Leg lengthening
Indications
|
|
The most common bones treated with lengthening procedures are the bones of the leg, the tibia and the femur.
Surgical treatment may be recommended for severe unequal leg lengths caused by:
- Poliomyelitis and cerebral palsy
- Small, weak (atrophied) muscles or short, tight (spastic) muscles may cause deformities and prevent normal leg growth
- Hip diseases such as Legg-Perthes disease
- Previous injuries or bone fractures that may stimulate excessive bone growth
- Abnormal spinal curvatures (scoliosis)
- Birth defects (congenital deformities) of bones, joints, muscles, tendons, or ligaments
|
Procedure
|
|
While the child is deep asleep and pain-free (using general anesthesia), the surgeons carefully study the blood vessels and blood supply to the bone.
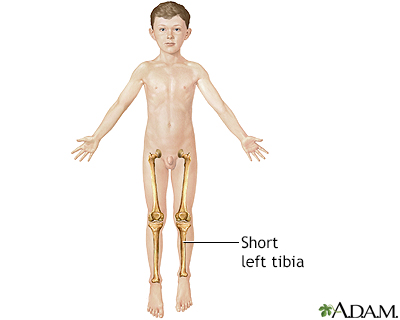
An incision is made in the bone to be lengthened; usually the lower leg bone (tibia) or upper leg bone (femur). Metal pins or screws are inserted into and through the skin and bone above and below the bone incision and the skin incision is stitched closed.
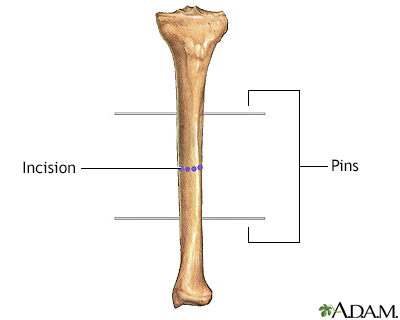
A metal device (such as an Ilizarov device) is attached to the screws in the bone and will be used later to gradually "crank" the cut bone apart, creating a space between the ends of the cut bone, which heals to form new bone. The lengthening device is used very gradually, lengthening the bone in extremely small steps, usually over the course of several months.
|
Aftercare
|
|
The device used to lengthen the leg after placement of the pins usually must stay in place for many months. The leg is gradually lengthened over this time, and the patient is usually able to walk with the device in place. Multiple surgeries are usually required to effect significant lengthening of the limb.
|
Review Date:12/12/2022
Reviewed By:C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency
or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional
should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911
for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they
do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.