Culdocentesis
Definition
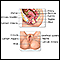
Culdocentesis is a procedure that checks for abnormal fluid in the space just behind the vagina. This area is called the cul-de-sac.
How the Test is Performed
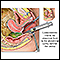
First, you will have a pelvic exam. Then, the health care provider will hold the cervix with an instrument and lift it slightly.
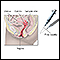
A long, thin needle is inserted through the wall of the vagina (just below the uterus). A sample is taken of any fluid found in the space. The needle is pulled out.
How to Prepare for the Test
You may be asked to walk or sit for a short time before the test is done.
How the Test will Feel
You may have an uncomfortable, cramping feeling. You will feel a brief, sharp pain as the needle is inserted.
Why the Test is Performed
This procedure is rarely done today because a transvaginal ultrasound can show fluid behind the uterus.
It may be done when:
- You have pain in the lower abdomen and pelvis, and other tests suggest there is fluid in the area.
- You may have a ruptured ectopic pregnancy or ovarian cyst.
- Blunt abdominal trauma.
Normal Results
No fluid in the cul-de-sac, or a very small amount of clear fluid, is normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Fluid may still be present, even if not seen with this test. You may need other tests.
A sample of fluid may be taken and tested for infection.
If blood is found in the fluid sample, you may need emergency surgery.
Risks
Risks include puncturing the uterine or bowel wall.
Considerations
You may need someone to take you home if you were given medicines to relax.
References
Braen GR, Kiel J. Gynecologic procedures. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 57.
Eisinger SH. Culdocentesis. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 161.
Hur HC, Lobo RA. Ectopic pregnancy: etiology, pathology, diagnosis, management, fertility prognosis. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 17.
Review Date:1/10/2022
Reviewed By:John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.