Alpha fetoprotein
Definition
Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the liver and yolk sac of a developing baby during pregnancy. AFP levels go down soon after birth. It is likely that AFP has no normal function in adults.
A test can be done to measure the amount of AFP in your blood.
Alternative Names
Fetal alpha globulin; AFP
How the Test is Performed
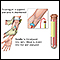
A blood sample is needed. Most of the time, blood is typically drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.
How to Prepare for the Test
You do not need to take any special steps to prepare.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel slight pain or a sting when the needle is inserted. You may also feel some throbbing at the site after the blood is drawn.
Why the Test is Performed
Your health care provider may order this test to:
- Screen for problems in the baby during pregnancy. (The test is done as part of a larger set of blood tests called quadruple screen.)
- Diagnose certain liver disorders.
- Screen for and monitor some cancers.
Normal Results
The normal values in males or nonpregnant females is generally less than 40 micrograms/liter.
The examples above are common measurements for results of these tests. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Greater than normal levels of AFP may be due to:
- Cancer in testes, ovaries, biliary (liver secretion) tract, stomach, or pancreas
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Liver cancer
- Malignant teratoma
- Recovery from hepatitis
- Problems during pregnancy
References
Driscoll DA, Simpson JL. Genetic screening and diagnosis. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 10.
Dugoff L, Wapner RJ. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital disorders. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 30.
Lee E. Neonatology. In: Anderson CC, Kapoor S, Mark TE, eds. The Harriet Lane Handbook. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 18.
Lee P, Jain S, Pincus MR, et al. Diagnosis and management of cancer using serologic and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 76.
Review Date:8/23/2023
Reviewed By:LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.