H influenzae meningitis
Definition
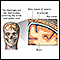
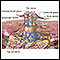
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
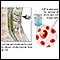
Bacteria are one type of germ that can cause meningitis. Haemophilus influenzae type b is one kind of bacteria that causes meningitis.
Alternative Names
H. influenzae meningitis; H. flu meningitis; Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis
Causes
H influenzae meningitis is caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b bacteria. This illness is not the same as the flu (influenza), which is caused by a virus.
Before the Hib vaccine, H influenzae was the leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children under age 5. Since the vaccine became available in the United States, this type of meningitis occurs much less often in children in the United States.
H influenzae meningitis may occur after an upper respiratory infection. The infection usually spreads from the lungs and airways to the blood, then to the brain area.
Risk factors include:
- Attending day care
- Cancer
- Ear infection (otitis media) with H influenzae infection
- Family member with an H influenzae infection
- Native American race
- Pregnancy
- Older age
- Sinus infection (sinusitis)
- Sore throat (pharyngitis)
- Upper respiratory infection
- Weakened immune system
Symptoms
Symptoms usually come on quickly, and may include:
- Fever and chills
- Mental status changes
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck (meningismus)
Other symptoms that can occur include:
- Agitation
- Bulging fontanelles in infants
- Decreased consciousness
- Poor feeding and irritability in children
- Rapid breathing
- Unusual posture, with the head and neck arched backwards (opisthotonos)
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. Questions will focus on symptoms and possible exposure to someone who might have the same symptoms, such as a stiff neck and fever.
If the doctor thinks meningitis is possible, a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is done to take a sample of spinal fluid for testing.
Other tests that may be done include:
- Blood culture
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the head
- Gram stain or other special stains, and culture of the spinal fluid
Treatment
Antibiotics will be given as soon as possible. Ceftriaxone is one of the most commonly used antibiotics. Ampicillin may sometimes be used.
Corticosteroids may be used to fight inflammation.
Unvaccinated people who are in close contact with someone who has H influenzae meningitis should be given antibiotics to prevent infection. Such people include:
- Household members
- Roommates in dormitories
- Those who come into close contact with an infected person
Outlook (Prognosis)
Meningitis is a dangerous infection and it can be deadly. The sooner it is treated, the better the chance for recovery. Young children and adults over age 50 have the highest risk for death.
Possible Complications
Long-term complications may include:
- Brain damage
- Buildup of fluid between the skull and brain (subdural effusion)
- Buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling (hydrocephalus)
- Hearing loss
- Seizures
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number or go to an emergency room if you suspect meningitis in a young child who has the following symptoms:
- Feeding problems
- High-pitched cry
- Irritability
- Persistent, unexplained fever
Meningitis can quickly become a life-threatening illness.
Prevention
Infants and young children can be protected with the Hib vaccine.
Close contacts in the same household, school, or day care center should be watched for early signs of the disease as soon as the first person is diagnosed. All unvaccinated family members and close contacts of this person should begin antibiotic treatment as soon as possible to prevent spread of the infection. Ask your provider about antibiotics during the first visit.
Always use good hygiene habits, such as washing hands before and after changing a diaper, and after using the bathroom.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Bacterial meningitis. www.cdc.gov/meningitis/bacterial.html. Reviewed July 15, 2021. Accessed November 10, 2022.
Nath A. Meningitis: bacterial, viral, and other. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 384.
Hasbun R, Van de Beek D, Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR. Acute meningitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 87.
Review Date:9/10/2022
Reviewed By:Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.