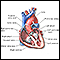
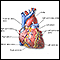
Myocardial contusion
Definition
Myocardial contusion is a bruise of the heart muscle.
Alternative Names
Blunt myocardial injury
Causes
The most common causes are:
- Car crashes
- Getting hit by a car
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
- Falling from a height, most often greater than 20 feet (6 meters)
Symptoms
A severe myocardial contusion may lead to signs and symptoms of a heart attack.
Symptoms can include:
- Pain in the front of the ribs or breastbone
- Feeling that your heart is racing
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may show:
- Bruise or scrapes on the chest wall
- Crunching sensation when touching the skin if there are rib fractures and puncture of the lung
- Fast heartbeat
- Irregular heartbeat
- Low blood pressure
- Rapid or shallow breathing
- Tenderness to the touch
- Abnormal chest wall movement from rib fractures
Tests may include:
- Blood tests (cardiac enzymes, such as Troponin-I or T or CKMB)
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the chest
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
These tests may show:
- Problems with the heart wall and the ability for the heart to contract
- Fluid or blood in the thin sac surrounding the heart (pericardium)
- Rib fractures, lung or blood vessel injury
- Problem with the heart's electrical signaling (such as a bundle branch block or other heart block)
- Fast heartbeat starting at the sinus node of the heart (sinus tachycardia)
- Abnormal heartbeat starting in the ventricles or lower chambers of the heart (ventricular dysrhythmia)
Treatment
In most cases, you will be closely monitored for at least 24 hours. An ECG will be done continually to check your heart function.
Emergency room treatment may include:
- Catheter placement through a vein (IV)
- Medicines to relieve pain, heart rate disturbances, or low blood pressure
- Pacemaker (temporary, may be permanent later)
- Oxygen
Other therapies may be used to treat a heart injury, include:
- Chest tube placement
- Draining blood from around the heart
- Surgery to repair blood vessels in the chest
Outlook (Prognosis)
People with a mild myocardial contusion will recover completely most of the time.
Serious heart injuries can increase your risk for heart failure or heart rhythm problems.
Prevention
The following safety tips may help prevent a heart bruise:
- Wear a seat belt when driving.
- Choose a car with air bags.
- Take steps to ensure safety when working at heights.
References
Boccalandro F, Shreyder K. Traumatic heart disease. In: Levine GN, ed. Cardiology Secrets. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 72.
Ledgerwood AM, Lucas CE. Blunt cardiac injury. In: Cameron AM, Cameron JL, eds. Current Surgical Therapy. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:1241-1245.
Raja AS. Thoracic trauma. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 38.
Review Date:5/8/2022
Reviewed By:Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
The Agency for Health Care Administration (Agency) and this website do not claim the information on, or referred to by, this site is error free. This site may include links to websites of other government agencies or private groups. Our Agency and this website do not control such sites and are not responsible for their content. Reference to or links to any other group, product, service, or information does not mean our Agency or this website approves of that group, product, service, or information.
Additionally, while health information provided through this website may be a valuable resource for the public, it is not designed to offer medical advice. Talk with your doctor about medical care questions you may have.